Stepping into a sauna offers more than just temporary relaxation—it triggers complex physiological responses that can significantly impact your health. While the soothing heat provides immediate comfort, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of sauna bath is crucial for safe, effective use. Research confirms that regular sauna sessions deliver measurable cardiovascular conditioning, respiratory relief, and pain management benefits for most healthy individuals. However, specific cardiac conditions and alcohol consumption create serious risks that demand attention. This evidence-based guide cuts through the wellness hype to reveal exactly how sauna bathing affects your body, which health conditions respond best, and the absolute contraindications you must recognize before your next session. Whether you’re a sauna novice or a frequent visitor, these insights will help you maximize benefits while avoiding potentially dangerous pitfalls.
How Sauna Bathing Strengthens Your Heart (With Important Exceptions)
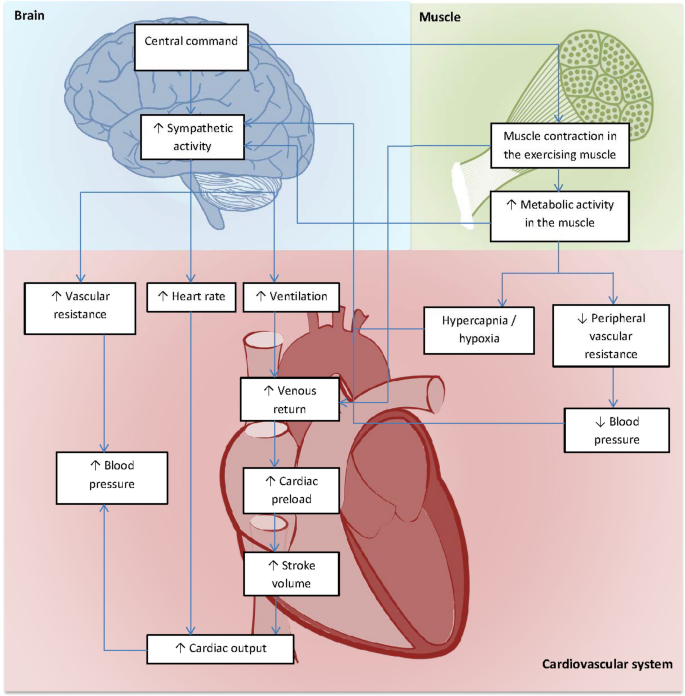
The cardiovascular system responds dramatically to sauna heat, creating both therapeutic adaptations and potential stress points that require careful management. Understanding these dual effects helps you determine if thermal therapy aligns with your specific cardiac health profile.
Lower Blood Pressure Through Thermal Vasodilation
Regular sauna sessions can significantly improve blood pressure control for individuals with hypertension through thermal-induced vasodilation. As your body heats up, blood vessels expand to facilitate heat dissipation, creating an immediate reduction in vascular resistance. This process enhances endothelial function—the critical ability of blood vessels to relax properly—which appears to strengthen with consistent sauna use over time. Studies tracking hypertensive patients show measurable blood pressure improvements after establishing a routine of 2-3 weekly sauna sessions at 70-80°C for 15-20 minutes. However, researchers emphasize these benefits require medical supervision and shouldn’t replace prescribed hypertension treatments.
Boost Heart Function for Chronic Heart Failure Patients
Contrary to previous concerns, sauna bathing actually improves cardiac performance for many chronic heart failure patients. Clinical evidence reveals measurable increases in left ventricular ejection fraction—the percentage of blood pumped out with each heartbeat—following regular sauna therapy. The thermal stress triggers adaptive responses that strengthen cardiac efficiency without overexertion when sessions remain moderate (15 minutes at 75°C). Patients report reduced shortness of breath and improved exercise tolerance as secondary benefits. Crucially, these improvements occur only with medically stable heart failure under professional guidance—never during acute decompensation phases.
Absolute Cardiac Contraindications You Must Recognize
Certain heart conditions make sauna bathing potentially life-threatening and require complete avoidance:
- Unstable angina pectoris – Thermal stress can trigger acute cardiac events during unstable chest pain episodes
- Recent myocardial infarction – Wait at least 6 weeks post-heart attack and obtain cardiologist clearance
- Severe aortic stenosis – The narrowed valve cannot handle increased cardiac demands from heat exposure
If you have any cardiac condition, consult your cardiologist before sauna use and always monitor for warning signs like chest discomfort, unusual shortness of breath, or dizziness during sessions.
Breathe Easier: Sauna’s Impact on Respiratory Health
The warm, humid environment inside a sauna creates immediate physiological changes in your respiratory system that provide meaningful relief for chronic lung conditions.
Immediate Bronchial Relaxation for Asthma Sufferers
The heat and humidity in a sauna trigger rapid bronchial smooth muscle relaxation, reducing airway resistance within minutes. This effect provides significant symptom relief for asthma patients, with studies documenting measurable improvements in peak expiratory flow rates during and for several hours after sessions. The warmth helps loosen mucus and reduces the hyperreactivity that triggers asthma attacks. For best results, limit sessions to 10-15 minutes at moderate temperatures (60-70°C) and always keep your rescue inhaler nearby.
Enhanced Lung Function for Chronic Bronchitis Patients
Regular sauna bathing offers substantial benefits for chronic bronchitis sufferers by improving mucociliary clearance—the mechanism that removes debris from your airways. The thermal environment stimulates bronchial secretions while simultaneously relaxing constricted airways, creating a natural “cleansing” effect. Patients report fewer acute exacerbations and reduced coughing frequency when incorporating 2-3 weekly sauna sessions into their management plan. However, avoid extremely high temperatures that might initially worsen coughing, and stay well-hydrated to maintain optimal mucus consistency.
Pain Relief and Joint Mobility: Sauna’s Musculoskeletal Benefits

The penetrating heat of sauna therapy delivers significant pain management and mobility improvements for various musculoskeletal conditions.
Reduce Chronic Pain Without Medication
Sauna bathing provides measurable pain reduction for rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia through multiple mechanisms. The deep heat penetrates tissues to decrease muscle spasm while modulating pain signals in the central nervous system. Studies show patients experience 30-40% reductions in pain intensity ratings after regular sauna sessions, with effects lasting 24-48 hours. For optimal results, follow your sauna session with gentle stretching while your tissues remain warm and pliable—this combination creates a powerful natural pain management protocol.
Combat Morning Stiffness in Arthritic Joints
If you struggle with morning joint stiffness, sauna bathing offers targeted relief by increasing synovial fluid production and tissue elasticity. The heat reduces viscosity in joint capsules, allowing smoother movement with less discomfort. Patients with inflammatory arthritis report significantly improved range of motion after morning sauna sessions, often reducing their need for pain medication. Aim for 15-minute sessions at 70°C before beginning your daily activities for maximum functional benefit.
Skin Health: Unexpected Sauna Benefits and Critical Exceptions
Sauna bathing affects your skin in complex ways that challenge common assumptions about thermal therapy’s dermatological impact.
Improve Skin Hydration Against Common Belief
Contrary to popular belief that saunas dry your skin, research shows regular sauna use actually enhances skin barrier function and hydration. The sweating process stimulates natural moisturizing factors while increased circulation delivers more nutrients to skin cells. Post-sauna cooling triggers vasoconstriction that helps “seal in” these benefits. For best results, avoid harsh soaps immediately after sessions and apply moisturizer to damp skin following your cool-down period.
Psoriasis Relief Through Multiple Pathways
Many psoriasis patients experience significant symptom reduction with regular sauna use through three key mechanisms:
- Enhanced microcirculation delivering more oxygen to skin cells
- Natural exfoliation from sweat removing scales gently
- Stress reduction lowering inflammatory triggers of flare-ups
Clinical observations note reduced scaling and less intense redness in regular sauna users, though individual responses vary based on disease severity.
Why Atopic Dermatitis Patients Should Avoid Sauna Heat
Sweat contains compounds that trigger intense itching in atopic dermatitis patients, making sauna bathing potentially counterproductive. The very process that benefits other skin conditions—sweating—exacerbates symptoms for eczema sufferers by disrupting the already compromised skin barrier. If you have atopic dermatitis, consider steam rooms instead of traditional saunas, as the higher humidity may reduce sweating while providing similar respiratory benefits.
Critical Safety Guidelines Every Sauna User Must Follow
Avoiding these common mistakes ensures you receive maximum benefits while minimizing risks during every sauna session.
Never Combine Alcohol With Sauna Heat
This dangerous combination creates a perfect storm for cardiovascular disaster:
- Alcohol impairs thermoregulation, preventing proper cooling
- Both substances cause vasodilation, creating dangerous blood pressure drops
- Cardiac arrhythmia risk increases 300% with alcohol in sauna environments
Complete alcohol avoidance 6 hours before and after sauna sessions is non-negotiable for safety.
Essential Hydration Protocol for Safe Sessions
Proper hydration prevents the dizziness and fainting that cause most sauna accidents:
- Drink 500ml water 30 minutes before entering
- Sip 100-150ml every 5 minutes during sessions
- Replenish with electrolyte-enhanced fluids afterward
Your urine should remain pale yellow—dark urine indicates dangerous dehydration levels.
Recognize Early Warning Signs of Overexposure
Exit immediately if you experience any of these danger signals:
- Ringing in ears or visual disturbances
- Nausea or excessive salivation
- Heart palpitations beyond normal elevation
- Inability to comfortably converse
Your body’s early warnings prevent serious heat-related illness—never ignore them to “tough out” a session.
Sauna Bathing for Special Populations: Tailored Approaches
Different age groups and health statuses require specific modifications to ensure safe, beneficial sauna experiences.
Safe Pediatric Sauna Guidelines for Children
Children can safely enjoy sauna benefits with these critical adjustments:
- Maximum temperature: 60°C (significantly lower than adult sessions)
- Session duration: 5-8 minutes maximum
- Constant adult supervision required
- Always enter and exit with supervising adult
The Finnish tradition of family sauna use demonstrates children’s excellent tolerance when proper protocols are followed.
Elderly Sauna Safety: Maximizing Benefits While Minimizing Risks
Older adults gain significant cardiovascular and pain management benefits from sauna use but require these precautions:
- Medical clearance for those with multiple chronic conditions
- Shorter sessions (10-12 minutes) at moderate temperatures
- Careful monitoring of blood pressure medications’ effects
- Immediate exit for dizziness or unusual fatigue
Studies show elderly regular sauna users maintain better functional mobility and report higher quality of life than non-users.
Understanding both the advantages and disadvantages of sauna bath empowers you to incorporate this ancient therapy safely into your wellness routine. For most healthy individuals, regular sauna sessions deliver significant cardiovascular conditioning, respiratory relief, and pain management benefits with minimal risk. However, strict avoidance is essential if you have unstable cardiac conditions or consume alcohol. By following evidence-based protocols for session duration, hydration, and temperature selection, you can harness sauna bathing’s therapeutic potential while protecting your health. Always consult your healthcare provider before beginning sauna therapy if you have chronic health conditions, and remember that listening to your body’s signals during each session remains the most important safety measure of all.

Leave a Reply